.NET CORE Interview Questions And Answers
1. What
is advantage of using.net core?
Fast - It is a lightweight,
high-performance web framework. Integration of Modern UI Framework - ASP.NET
Core support modern, a Client-side framework like AngularJs, ReactJs and React
with Redux etc.
Hosting - It has the ability to host on IIS,
Apache, Docker or Self Hosting.
Cross
Platform - ASP.NET
Core web application can run on Windows, Mac, Linux development tools.
Support
Built-In Dependency Injection -
It supports built-in Dependency Injection.
Supports
Modular - It support
modular HTTP request.
Open-Source - It is an open-source and
community-focused web framework.
Side-by-side
app versioning -
ASP.NET Core runs on .NET Core which supports the simultaneous running of
multiple versions of applications.
A unified
story for building web UI and web APIs.
2. How
was the architecture of your .Net Core application?
ASP.NET Core is
that the main business logic and UI logic are encapsulated in ASP.NET Core Web
App layer, while the database access layer, cache services, and web API
services are encapsulated in infrastructure layer and common utilities,
objects, interfaces and reusable business services are encapsulated as
micro-services in application core layer.
3.
What is Startup class in .net core?
·
It configures the application's services and
defines the middleware pipeline.
·
Startup is entry point to the application,
setting up configuration and wiring up services the application will use. It
defines the app's request handling pipeline as a series of middleware
components.
4.
What is the purpose of the Startup class?
Startup class
handles two important aspects of your application,
·
service
registration
·
middleware
pipeline
5.
What is Difference between ConfigureServices and Configure methods?
|
ConfigureServices() |
Configure() |
|
used to register
services |
configure
components within the request pipeline. |
|
takes a parameter
of type IServiceCollection. |
takes a parameter
of type IApplicationBuilder with possible parameters of any Service
which is registered in the ConfigureServices() method. |
|
an application
should contain an ConfigureServices() |
optional Configure()
method. |
6.
What is the role of ConfigureServices and Configure method?
ConfigureServices
ConfigureServices gets
called by the host before the 'Configure' method to configure the app's services.
ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
Configure
Configure method
is used to add middleware components to the IApplicationBuilder instance
that's available in Configure method. Configure method also specifies how
the app responds to HTTP request and response. This method gets called by
the runtime. This method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
Configure(IApplicationBuilder app,
IWebHostEnvironment env)
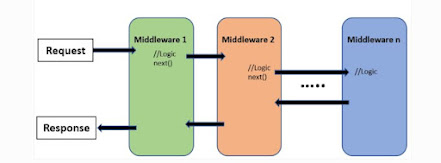
7.
Explain the concept of middleware in ASP.NET Core?
ASP.NET Core,
middleware refers to the C# classes that manipulate an HTTP request when it
comes in or an HTTP response when it’s on its way out. For example,
·
Generate
an HTTP response for an incoming HTTP request
·
Intercept
and make changes to an incoming HTTP request and pass it on to the next piece
of middleware.
· Intercept and make changes to an outgoing HTTP response, and pass it on to the next piece of middleware.
Middleware used for logging, security, authentication, authorization, etc.
8. Why
we use Middleware in .net core? In .net framework how did we handled the
functionality of middleware?
·
Middleware
controls how our application responds to HTTP requests.
·
Middleware
control how our application looks when there is an error.
·
Middleware
is a key piece in how we authenticate and authorize a user to perform specific
actions.
9.
How do you create a Custom Middleware in .Net Core?
1.
Create
new Middleware class and add logic(for example logging logic).
2.
Inside
Configure method add below line.
app.UseMyMiddleware(); OR app.UseMyMiddleware(Middderwarename);
10. Difference
between app.Use() and app.Run() in .NET Core?
app.Run() will end the request.
app.Use() will pass the request to next middleware.
11. What is
Routing in Asp.Net Core?
Routing is
functionality that map incoming request to the route handler. The route can
have values (extract them from URL) that used to process the request.
· Conventional
routing
· Attribute
routing
12. What
is the purpose of the wwwroot folder?
wwwroot folder
contains static files and compiled assets, such as JavaScript, CSS, and images that
your web application needs. wwwroot is the only folder in the entire project
that's exposed as-is to the browser.
13. What
is launchsetting.json, appsetting.json, packages.json file in .NET
Core?
launchsetting.json:
This json file holds project specific settings associated with each debug
profile, Visual Studio is configured to use to launch the application,
including any environment variables that should be used. You can define
framework for your project for compilation and debugging for specific profiles.
This file is placed in Properties folder.
appsetting.json:
The appsettings.json file is an application configuration file used to
store configuration settings such as database connections strings, any
application scope global variables, etc.
Package.json:
package.json file is the heart of any Node project. It records important
metadata about a project which is required before publishing to NPM, and also
defines functional attributes of a project that npm uses to install
dependencies, run scripts, and identify the entry point to our package.
14. What
is Dependency Injection? Types of Dependency Injection?
ASP.NET Core
comes with a built-in Dependency Injection framework that makes configured
services available throughout the application. You can configure the services
inside the ConfigureServices method as below.
services.AddScoped();
services.AddSingleton();
services.AddTransient();
Types of Dependency
Injection:
1.
Constructor
Injection: the injector
supplies the service (dependency) through the client class constructor.
2.
Property
Injection: the
injector supplies the dependency through a public property of the client class.
·
Using
the [Dependency] attribute
·
Using
run-time configuration
//run-time configuration
container.RegisterType<Driver>(new
InjectionProperty("Car", new BMW()));
3. Method Injection: the client class implements an interface which declares the method(s) to supply the dependency and the injector uses this interface to supply the dependency to the client class.
15. What
is AddSingleton, AddTransient, AddScoped?
AddSingleton() - Singleton service is created only
one time per application and that single instance is used throughout the
application life time.
AddTransient() - Transient service is created each
time it is requested.
AddScoped() - Scoped service is created once per
request within the scope.
16. Describe
the Service Lifetimes.
Singleton - Service with singleton lifetime is
created once when first time the service is requested. For subsequent requests
same instance is served by service container.
Example:
Services.AddSingleton(IEmployee,
EmployeeService);
Transient - Services with transient lifetime are
created each time they are requested from service container. So, it's best
suited for stateless, light weight services.
Example:
Services.AddTransient(IEmployee,
EmployeeService);
Scoped - Services with scoped lifetime are
created once per connection or client request. When using scoped service in
middleware then inject the service via invoke or invokeAsync method. You should
not inject the service via constructor injection as it treats the service behaviour
like Singleton.
Example:
Services.AddScoped(IEmployee,
EmployeeService);
17. How
do we enable session in .net core?
1.
We need
call "services.AddSession()" method in ConfigureServices method
of startup class.
2.
app.UseSession(); // add this line inside
Configure Method
18. How
Configuration works in ASP.NET Core?
Configuration is
implemented using various configuration providers.
·
appsettings.json
- settings file
·
Azure
Key Vault
·
Environment
variables
·
In-memory
.Net objects
·
Command
Line Arguments
·
Custom
Providers
By default apps
are configured to read the configuration data from appsettings.json,
environment variables, command line arguments etc.
19. How
to use multiple environments in ASP.NET Core?
ASP.NET Core use
environment variables to configure application behavior based on runtime
environment. launchSettings.json file sets ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT to
Development on local Machine.
20. Explain
Session and State management in ASP.NET Core?
As we know HTTP
is a stateless protocol. HTTP requests are independent and does not retain user
values. There are different ways to maintain user state between multiple HTTP
requests.
·
Cookies
·
Session
State
·
TempData
·
Query
strings
·
Hidden
fields
·
HttpContext.Items
·
Cache
21. What
is Memory Leak in .Net Core?
A memory leak may
happen when your app references objects that it no longer needs to perform the
desired task. Referencing said objects makes the garbage collector to be unable
to reclaim the memory used, often resulting in performance degradation and potentially
end up throwing a OutOfMemoryException.
22. What is
Metapackages?
The framework .NET
Core 2.0 introduced Metapackage that includes all the supported package by
ASP.NET code with their dependencies into one package. It helps us to do fast
development as we don't require to include the individual ASP.NET Core
packages. The assembly Microsoft.AspNetCore.All is a meta package
provide by ASP.NET core.
23. While
calling an API I want to apply some policies, so how would you that in .Net
Core?
Inside
ConfigureServices add below line:
services.AddCors(c
=>
{
c.AddPolicy("AllowOrigin",
options => options.AllowAnyOrigin());
});